How Ordinox Works
Ordinox is a Cosmos app chain that operates using state pegs. Every node in the Ordinox network operates a full Bitcoin-core node, an OPI BRC20 indexer, Runes Indexer, Electrum Indexer and an Ethereum (Any alt-EVM) full node.
This setup allows each node to manage vaults on these decentralized networks efficiently. Here's a breakdown of the key components of Ordinox:
Observer
This is a custom-built core client that connects Ordinox to the networks it supports. It is responsible for handling communication between Ordinox and other blockchains. Here's the breakdown:
- DepositObserver: Observes the deposit queue and helps validators sign on-chain messages regarding deposit verification. A deposit is confirmed only if 2/3 of the validators sign off on it on-chain. This can be witnessed using the deposit-tx-id.
- WithdrawObserver: Observes the withdrawal queue and helps validators create, sign (TSS), and broadcast messages to the target chain. This process is explained in the Application Flow page.
- Relayer: An API server that helps full nodes and validators submit messages on-chain. It is used by RPC providers and others who want to provide a public service without requiring users to use a Kepler wallet.
- Verifier: Responsible for verifying the legitimacy of a deposit transaction. It handles edge cases for various chains and protocols and considers long block times before verifying. All validators should run a full node of all the chains Ordinox supports, along with any additional indexing software required for verification (OPI, Electrum, etc.).
- Emitter: Responsible for building transactions which will be signed by the TSS module and broadcasted to the target chain.
- TSS: This is the audited implementation of GG20 TSS maintained by ThorChain, which lets validators generate new vaults (vault rotation) and sign WithdrawTx(s).
TSS Protocol
The Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) protocol is a crucial part of Ordinox's security framework. It allows Ordinox validators to approve transactions without revealing their individual private keys to each other. This protocol is key to ensuring the decentralized and secure nature of the platform. Ordinox currently uses an implementation of TSS developed and maintained by ThorChain. This implementation has been battle-tested for over 4 years and has been managing over 100M in weekly trade volume on ThorChain, with a network of over 100 independent and anonymous validators who rotate periodically.
Cosmos Module for Managing App State (State Machine)
This module keeps the Ordinox app chain running smoothly. It manages the application's state, ensuring that all transactions and swaps are accurately recorded and that the system remains stable and reliable. All the state pegs and balances from other chains are tracked in this Cosmos module.
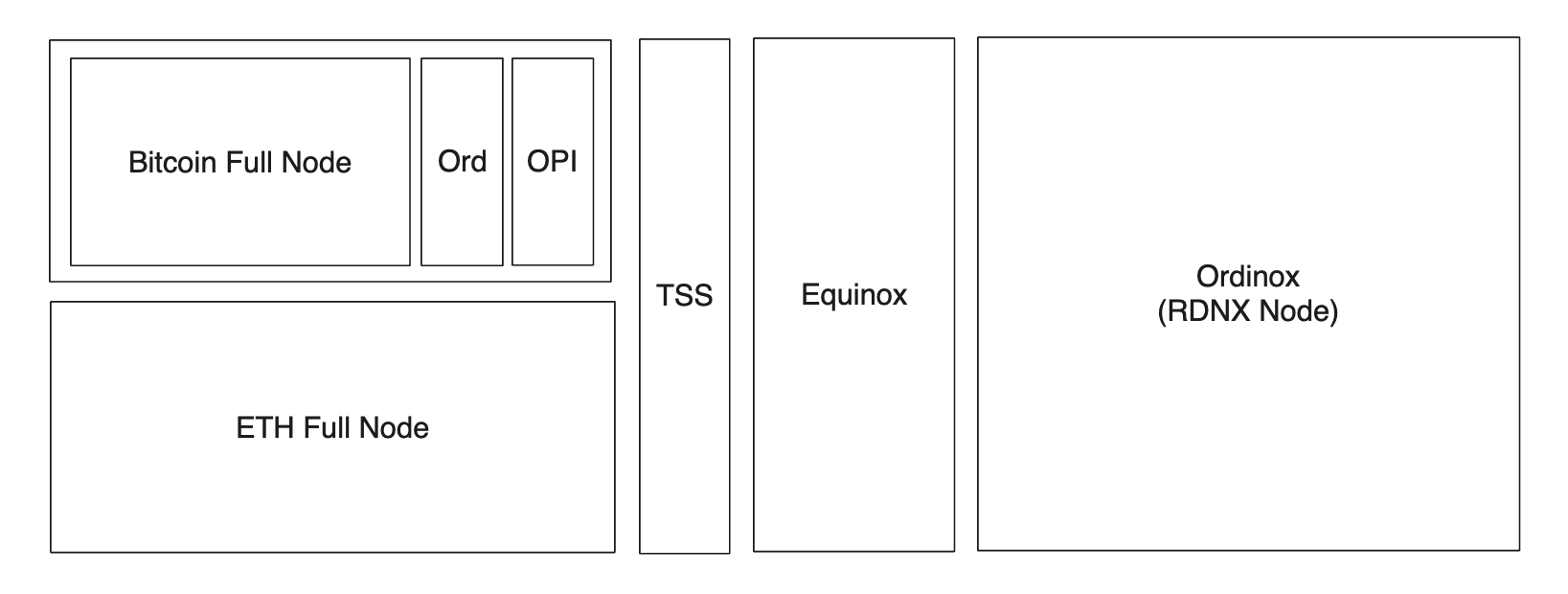
Ordinox Network
The Ordinox Network is a dedicated app chain built using the Cosmos SDK, tailored for managing liquidity pools, executing swaps, and overseeing liquidity additions and removals. Designed with the future in mind, it aims to extend its capabilities to support a range of DeFi activities centered around Bitcoin-based tokens.
The state of the Ordinox app chain is structured to capture all essential aspects of its operation, as outlined in the GenesisState struct. This struct includes several key fields:
- Params: Chain Params, controlled by the governance module.
- PoolList: An array of liquidity pools available on the network. Each pool is represented by the Pool struct, which contains the details necessary for managing the liquidity within.
- LiquidityProviders: A list of LiquidityProvider structs, identifying individuals or entities that supply liquidity to the pools.
- POL (Protocol Owned Liquidity): An array of ProtocolOwnedLiquidity structs, representing the liquidity owned directly by the Ordinox protocol itself.
- Assets: A list of assets supported by the network. This usually contains the decimal points allowed and the chain it belongs to. This too is controlled by the governance module.
- Deposits: An array of deposits done into the network .
- Commands: An array of commands executed by users in the network.
- Balances: An array of balances users' addresses carry.
- Withdrawals: An array of withdrawals executed by users on the network.
type ChainState struct {
Params Params `protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=params,proto3" json:"params"`
PoolList []Pool `protobuf:"bytes,5,rep,name=pool_list,json=poolList,proto3" json:"pool_list"`
LiquidityProviders []LiquidityProvider `protobuf:"bytes,10,rep,name=liquidity_providers,json=liquidityProviders,proto3" json:"liquidity_providers"`
POL []ProtocolOwnedLiquidity `protobuf:"bytes,13,rep,name=POL,proto3" json:"POL"`
Assets []common.Asset `protobuf:"bytes,15,rep,name=assets,proto3" json:"assets"`
Deposits []DepositTx `protobuf:"bytes,16,rep,name=deposits,proto3" json:"deposits"`
Commands []Command `protobuf:"bytes,17,rep,name=commands,proto3" json:"commands"`
Balances []Balance `protobuf:"bytes,18,rep,name=balances,proto3" json:"balances"`
Withdrawals []WithdrawTx `protobuf:"bytes,19,rep,name=withdrawals,proto3" json:"withdrawals"`
}